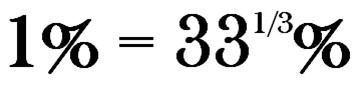
The Bank of Canada’s December 2025 announcement held its target for the overnight rate at 2.25%
Inflation has been close to the Bank’s 2% target for more than a year, with October’s reading at 2.2%, but core inflation remains closer to 2.5%, showing that some underlying price pressures still need time to settle.
Economic growth looked stronger in the third quarter, but much of that increase came from trade-related swings rather than a broad pickup in household or business spending. Employment has improved slightly, bringing the unemployment rate down to 6.5%, yet hiring plans remain cautious and several key industries continue to face challenges. Overall, the data point to an economy finding its footing slowly, and many households are still feeling tight cash flow even as inflation cools.
The Bank Rate remains at 2.5% and the deposit rate remains at 2.20%
Five smart moves to make for your debt today:
- Refresh the budget. Re-run your numbers with today’s payment amounts and see how much you can redirect toward high-interest balances.
- Build a buffer. Ask yourself: Could I still handle my payments if prime rose by 0.50 %? If not, start padding an emergency fund or accelerating principal payments.
- Press pause on new debt. A rate hold is not a green light to take on more credit—especially high-interest “buy now, pay later” or payday alternatives.
- Consider fixing your rate. If a predictable payment helps you sleep, compare current five-year fixed offers with your variable rate and the break-even costs of switching.
- Get professional help early. A free conversation with an Ontario Licensed Insolvency Trustee can show whether strategies like consolidation or a consumer proposal could cut interest and keep payments affordable.
| Bank Rate Changes Since 2010 | Target Overnight Rate | Change |
| May 31st, 2010 | 0.50% | 0.25 |
| July 19, 2010 | 0.75% | 0.25 |
| September 7, 2010 | 1% | 0.25 |
| January 20, 2015 | 0.75% | -0.25 |
| July 14, 2015 | 0.50% | -0.25 |
| July 11, 2017 | 0.75% | 0.25 |
| September 5, 2017 | 1% | 0.25 |
| January 16, 2018 | 1.25% | 0.25 |
| July 10, 2018 | 1.50% | 0.25 |
| October 23, 2018 | 1.75% | 0.25 |
| March 3, 2020 | 1.25% | -0.50 |
| March 15, 2020 | 0.75% | -0.50 |
| March 26, 2020 | 0.25% | -0.50 |
| March 2, 2022 | 0.50% | 0.25 |
| April 13, 2022 | 1.00% | 0.50 |
| June 1, 2022 | 1.50% | 0.50 |
| July 13, 2022 | 2.50% | 1.00 |
| September 7, 2022 | 3.25% | 0.75 |
| October 26, 2022 | 3.75% | 0.50 |
| December 7, 2022 | 4.25% | 0.50 |
| January 25, 2023 | 4.50% | 0.25 |
| June 7, 2023 | 4.75% | 0.25 |
| July 12, 2023 | 5.00% | 0.25 |
| June 5, 2024 | 4.75% | -0.25 |
| September 4, 2024 | 4.25% | -0.25 |
| October 23, 2024 | 3¾% | -0.50 |
| December 11, 2024 | 3½% | -0.50 |
| January 29, 2025 | 3.00% | -0.25 |
| March 12, 2025 | 2.75% | -0.25 |
| September 17, 2025 | 2.50% | -0.25 |
| October 29, 2025 | 2.25% | -0.25 |
When the Bank of Canada lowers rates, banks and mortgage lenders usually follow with reduced borrowing costs. Here’s what a 25-basis point drop can do for a mortgage:
If you have a $400,000 mortgage, amortized over 25 years, at 2.59%, your monthly payment is $1,810. A reduction to 2.34% would bring your payment down to $1,760.
That’s a $50 decrease each month.
Though the decrease is smaller than the impact of an increase, over time, this savings adds up. A reduced monthly payment can free up cash flow, giving you some breathing room or more room for savings (so- don’t take on more debt!)
In the long run, lower interest rates can also reduce the total interest you pay over the life of your loan.
How much does a 25-basis point increase in interest rates cost?
Every time the Bank of Canada raises rates, banks and mortgage companies follow with increased mortgage rates. Here is the impact of a 25-point increase on a small mortgage.
If you have a $400,000 mortgage, amortized over 25 years, at 2.59%, your monthly mortgage payment would be $1,810 per month.
That same $400,000 mortgage at 2.84% would cost you $1,860 per month.
That’s an increase in your monthly mortgage payment of $50 a month.
Multiply this by the 5 rate increases some economists are predicting, and you are facing a possible increase in your mortgage payment of $250 a month.
With so many Canadians living paycheque to paycheque, this is going to be a shock. Yet, we shouldn’t be surprised.
In 2012, I was interviewed on CBC Radio’s The Current, on a segment about Doubting Personal Debt and we discussed, even way back then, that debt is a “ticking time bomb”. Back then I warned that low interest rates were making our debt artificially ‘affordable’. I made the comment that we could be in trouble if interest rates rise.
And on the same day in October 2018 as the Bank of Canada increased rates to the highest since December 2008, I was once again on CBC Radio’s The Current to talk about Canadian debt as part of a special they were calling Debt Nation.
When facing a rising rate environment, you need to consider what an increase in interest rates will do to your personal cash flow.
For many years the best decision a Canadian could make was to get a variable rate mortgage (not a fixed rate), because the rate was lower. That’s great, but a variable rate, obviously, is variable, so it can go down, but it can also go up.
Today you may be paying 3% on your variable rate mortgage, so on a $200,000 mortgage amortized over 25 years you are making a monthly payment of $946.40. What happens if your variable interest rate were to increase by 1%? Again, you may not think 1% is a big number, but a 4% interest rate on your $200,000 mortgage amortized over 25 years would cost you $1,052.04 per month. Can you afford to pay an extra $105.55 per month on your mortgage? Will your after-tax paycheque be increasing by $105 per month this year? If not, higher interest rates will squeeze your budget.
Here’s where most people miss the point: going from a 3% to a 4% interest rate is not an increase of 1% in your payments. If your rent goes from $300 to $400 per month, how much did your rent increase? Answer: one third, or over 33%.
That’s the point: if your interest rate increases by 1%, the actual interest cost of your mortgage in the example above increased by over 33%.
That’s a huge increase, and unless your pay will also be going up by 33%, higher interest rates will be a problem for your monthly cash flow.